We spend most of our working days sitting down in our office chairs, but few people know about the mechanics that make them work so effortlessly.
As you consider buying a new chair, which features matter to you? Would you like adjustable options, touches of extra comfort, or the very latest technology? How about all of the above?
From seats and backrests to lumbar support and levers, here’s a breakdown of the office chair parts that make ergonomic seating an awesome feat of engineering. Discover the features that should be at the top of your wishlist:
Important parts of an ergonomic chair
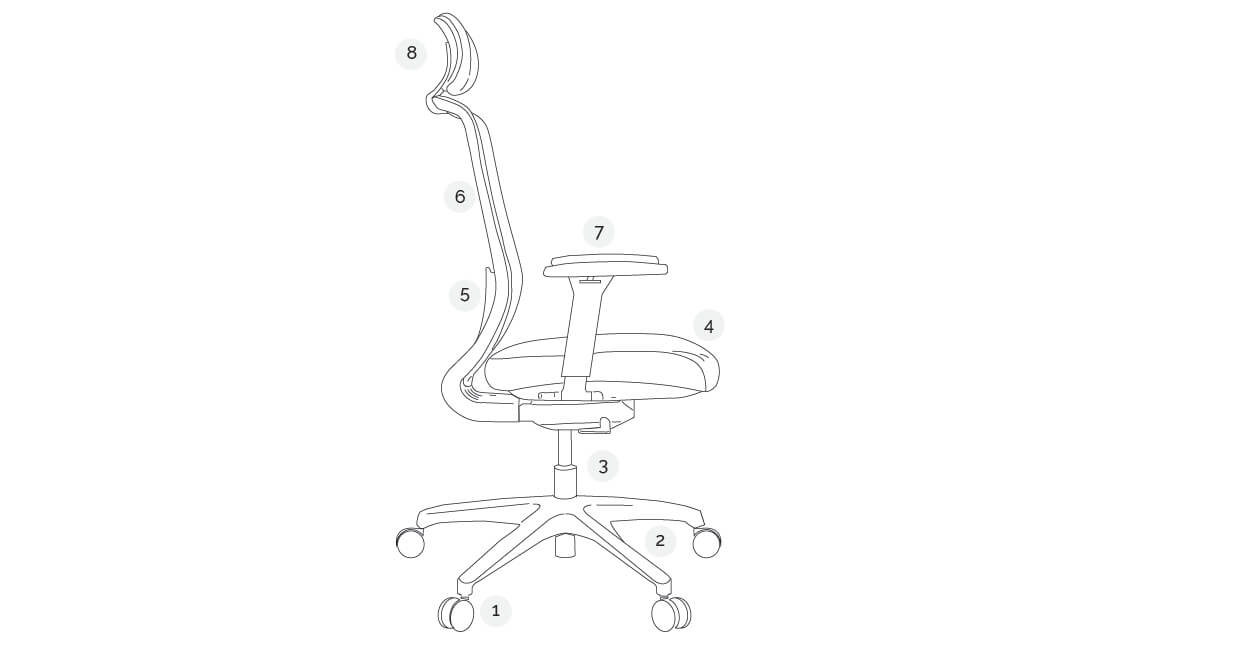
- Castors
- Base
- Cylinder and Gas Lift
- Seat
- Lumbar Support System
- Backrest
- Armrests
- Headrest
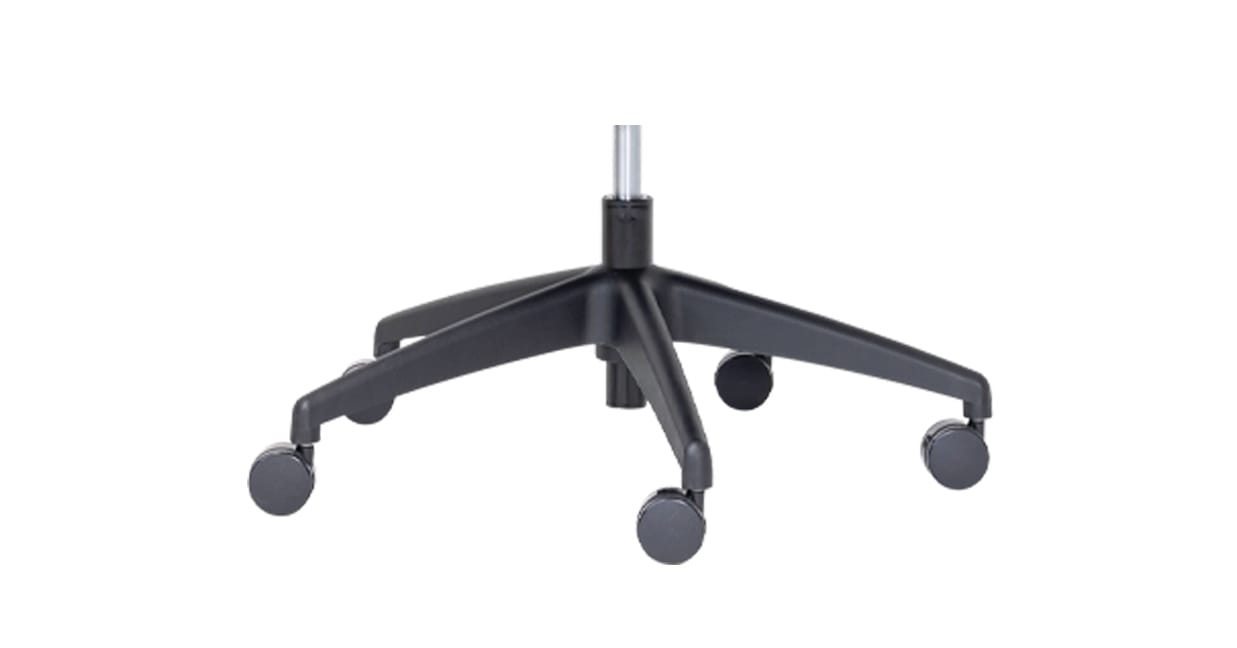

1. Castors
Let’s start from the bottom. Castors are small wheels, usually 60mm in diameter, fixed to the bottom of your chair that help you move around freely.
Hard wheel castors work well on carpeted floors while soft wheel castors are great on extra hard surfaces as they move more smoothly and make less noise.
Twin Wheel
Twin wheel castors have two wheels instead of one for extra manoeuvrability. Designed for an easy swivel action, twin wheel castors also help prevent damage to carpets.
Most of our office chairs come with hard 60mm twin wheel castors, which can be swapped out for customised soft PU castors.
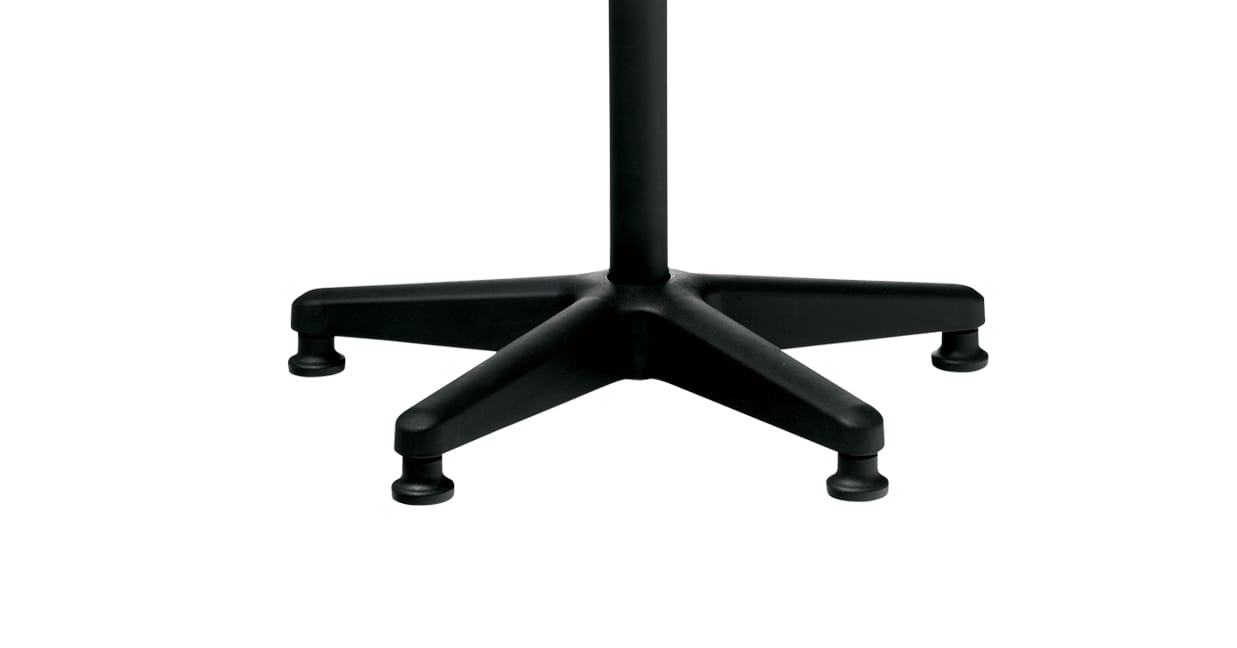

Glides
Chairs without castors usually have glides. Made out of metal and plastic, glides are a good option if you don’t want your chair to roll around, and popular for healthcare workplaces.
The Buro Bambach Saddle Seat, Buro Posturite and Buro Polo stools include optional glides.
Locking
Locking castors control the movement of your office chair, and can be fixed in place to keep feet still. There are weight-on or weight-off castors. Weight-on castors are the most popular, they lock when you're sitting on the chair, so you stay fixed while the chair is in use. Whereas weight-off castors lock when you're not sitting on the chair.

Example: Buro Metro - Ali Base and Buro Metro - Nylon Base
2. Base
The structure that keeps the rest of the chair steady while holding your body weight. Bases are usually made from nylon or aluminium. Models such as the Buro Persona feature heavy-duty bases with a mix of glass fibre added to the base to maximise strength and support.
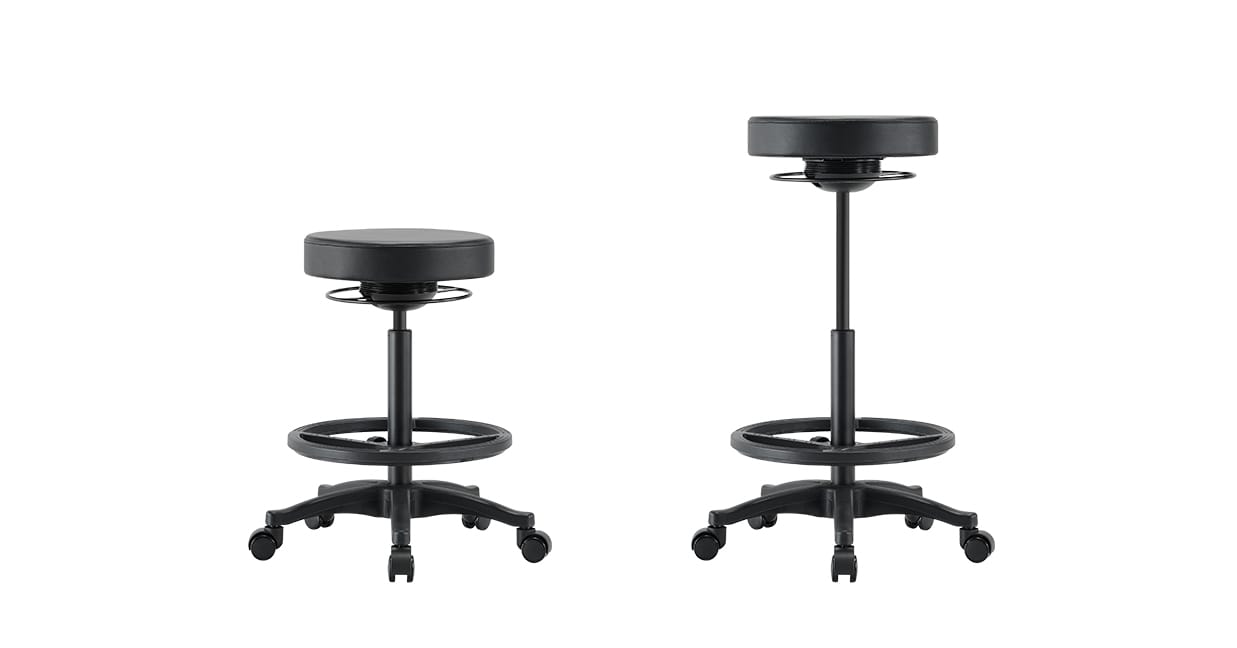

Example: Buro Polo Drafting Stool
Architectural base
Architectural bases or drafting bases are designed for people working at higher desks and benches. They have a higher cylinder and a foot ring to rest your feet on. They’re a great option in the office if you prefer to stand and want a quick transition to perching height rather than down to a sitting height.
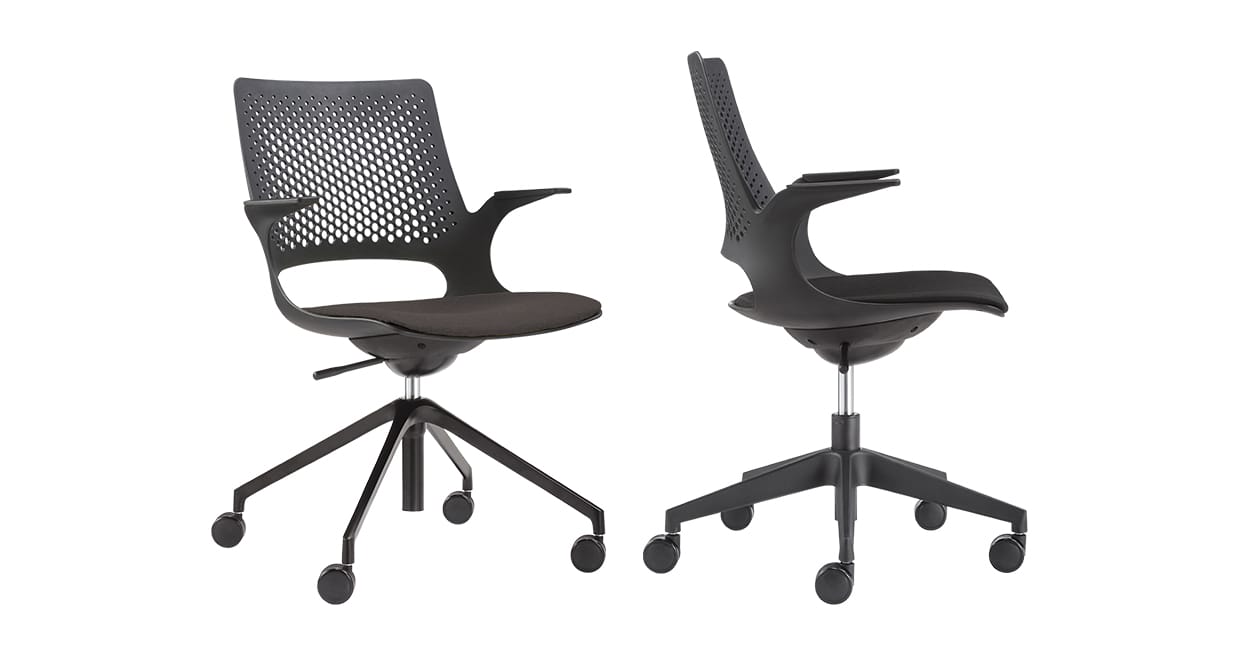

Example: Konfurb Harmony 4 Star Base and Konfurb Harmony 5 Star Base
A five-star base has five points and five castors, and a four-point base has one fewer.

Example: Buro Metro II – Ali Base
3. Cylinder and Gas lift
The cylinder connects the seat and the base and works in harmony with the gas lift to raise or lower your chair. It often comes with a cylinder cover to protect against dust.
A gas lift allows you to adjust the height of your seat with a simple lever. A cylinder filled with compressed gas is the key part of the mechanism.
Gas cylinders take the pressured power of compressed gas and force it through a chamber which then moves a piston in the required location. This movement and force enable your seat to move up or down.

Example: Buro Roma – 3 Lever Mid Back
4. Seat
Your seat is made from high-quality foam for maximum comfort and support. High-density polyurethane moulded foam is the best you can get, while high-density quality seat foam and dual foam are also comfortable.
Seat upholstery can be made from fabric, leather, elastic, or a combination of these materials.
Waterfall edge seating
Waterfall edge seats feature a rounded front that slopes downward and moulds to a user’s body. They reduce tension at the back of the thighs and help to distribute weight evenly.
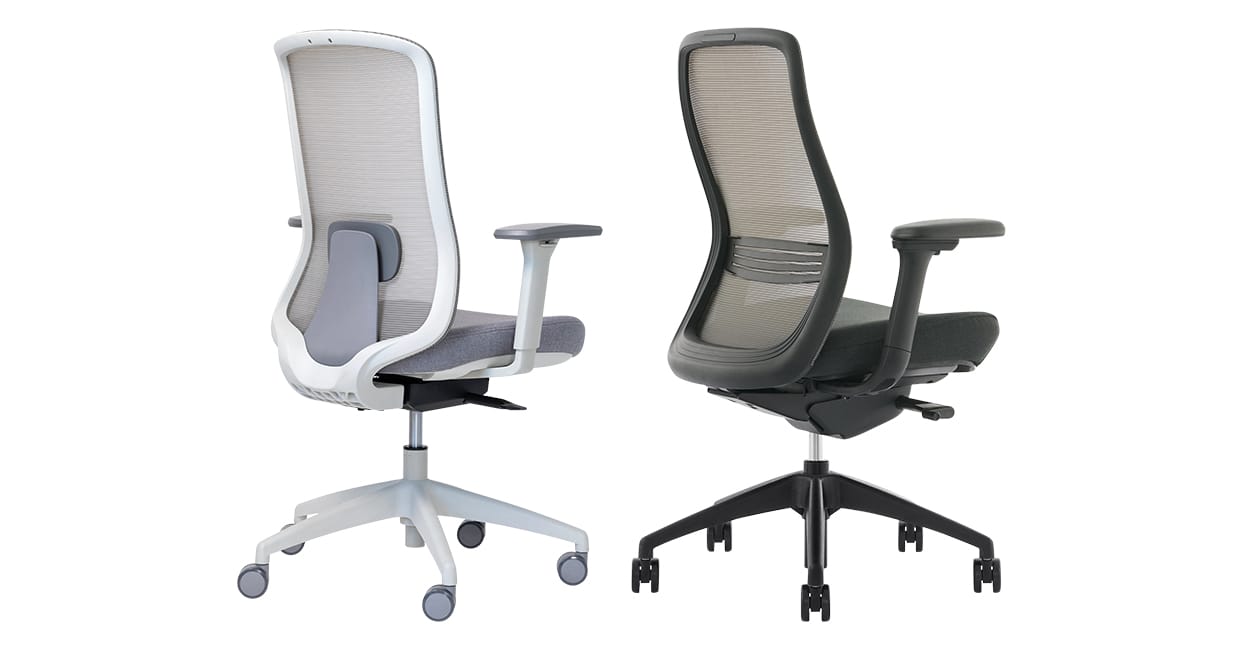

Example: Buro Elan and Konfurb Luna
5. Lumbar support system
Lumbar support is the apparatus that supports the lumbar region of your lower back while you are seated. This support maintains the natural curve of your spine with padding, preventing back pain and injuries.
Some chairs have height-adjustable lumbar support and others also offer depth-adjustable lumbar support.
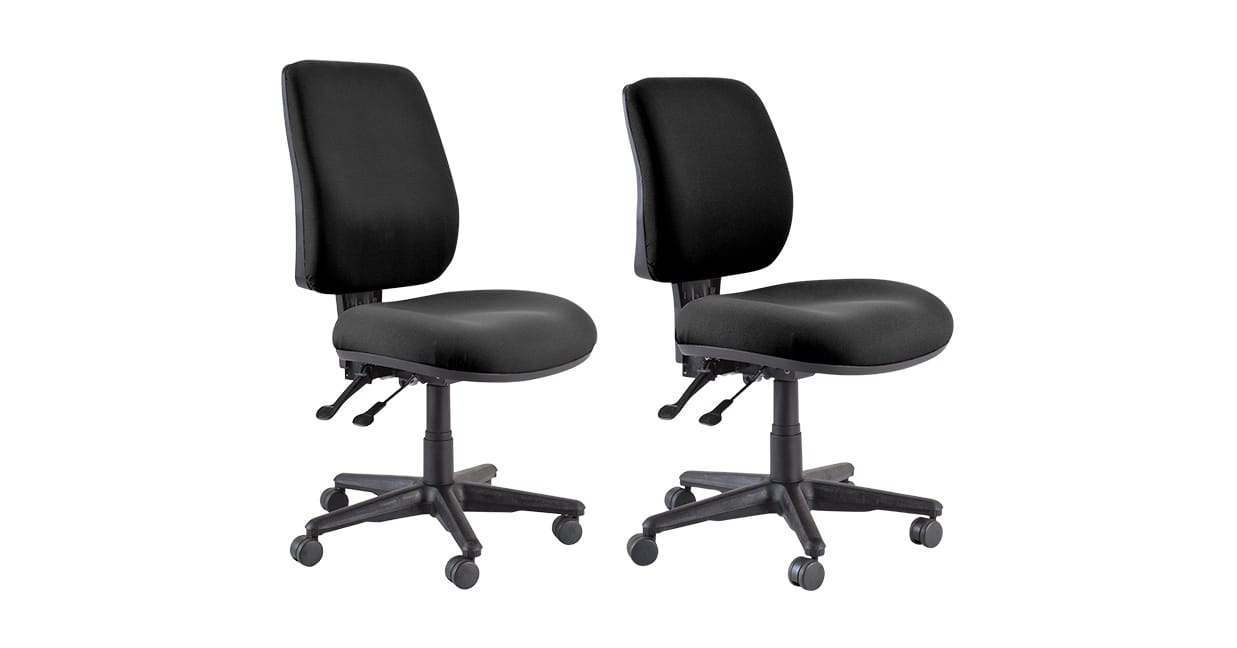

Example: Buro Roma 2L High Back and Buro Roma 2L Mid Back
6. Backrests
Backrests, like seats, are filled with high-quality foam and covered in fabric or leather to ensure they are as comfortable as possible.
Types of backrest
There are different types of backrest to suit different body shapes.
A mid back is an allrounder well suited to the average body shape, while a high back is a great option for taller people.
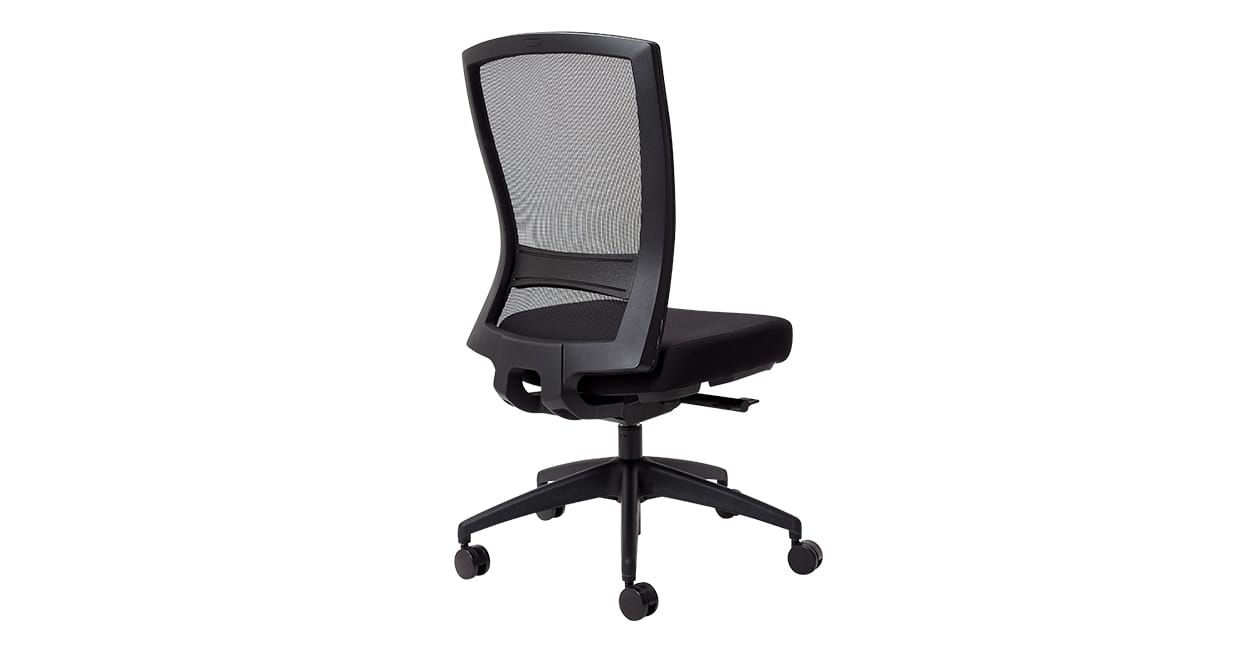

Example: Buro Mentor
While many backrests are upholstered with fabric or leather, mesh back chairs like the Buro Mentor Mesh Back and the much loved Buro Metro family) offer support and breathability. Mesh backs are often favoured in hotter climates as they encourage airflow around the body.
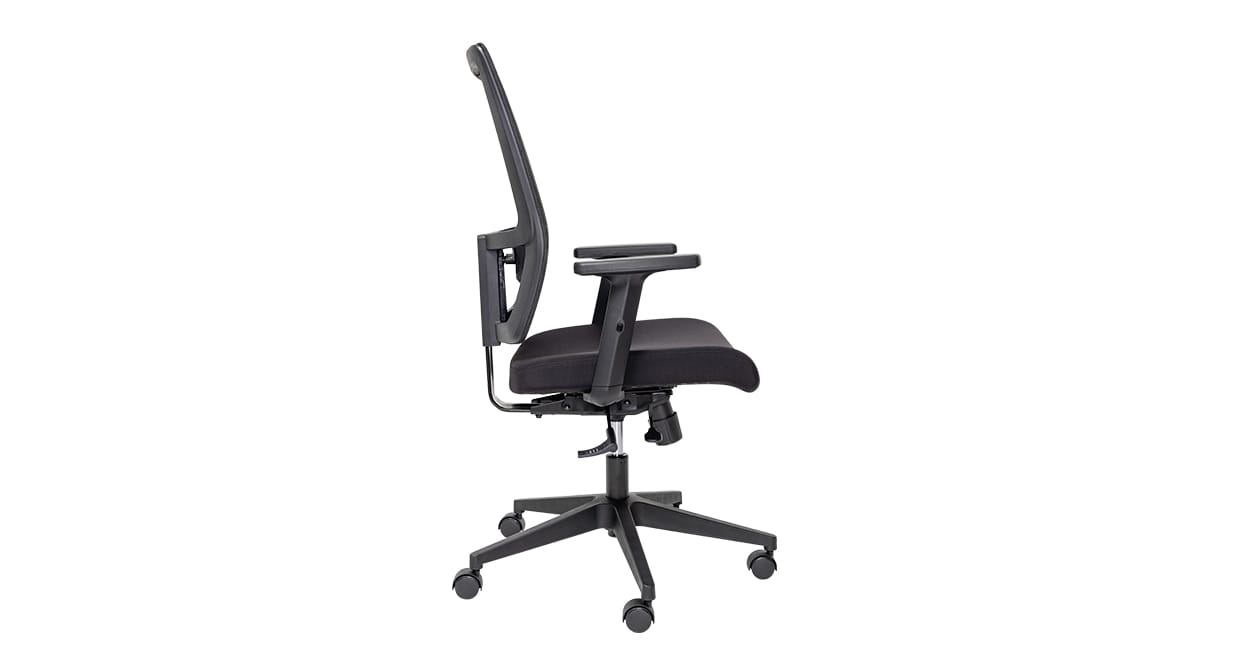

Example: Buro Mantra
7. Arms
Many office chairs come without armrests and arm pads, but for people who prefer something to rest on, armrests offer an extra layer of luxury and support.
Armrests are great for extra support when using your mouse, taking the weight off your shoulders and neck. They're also helpful for getting on and off your chair if you've got hip or knee problems.
The old chair arms got a bad rap when they were fixed height and lacked adjustments. Buro’s armrests are adjustable, giving you ergonomic support for every task.
Some chairs like the Buro Mantra, have optional height-adjustable and width-adjustable armrests.
Premium chairs like the Konfurb Luna have optional add-ons including 4D arms, with width, depth and height-adjustable arms for maximum manoeuvrability.
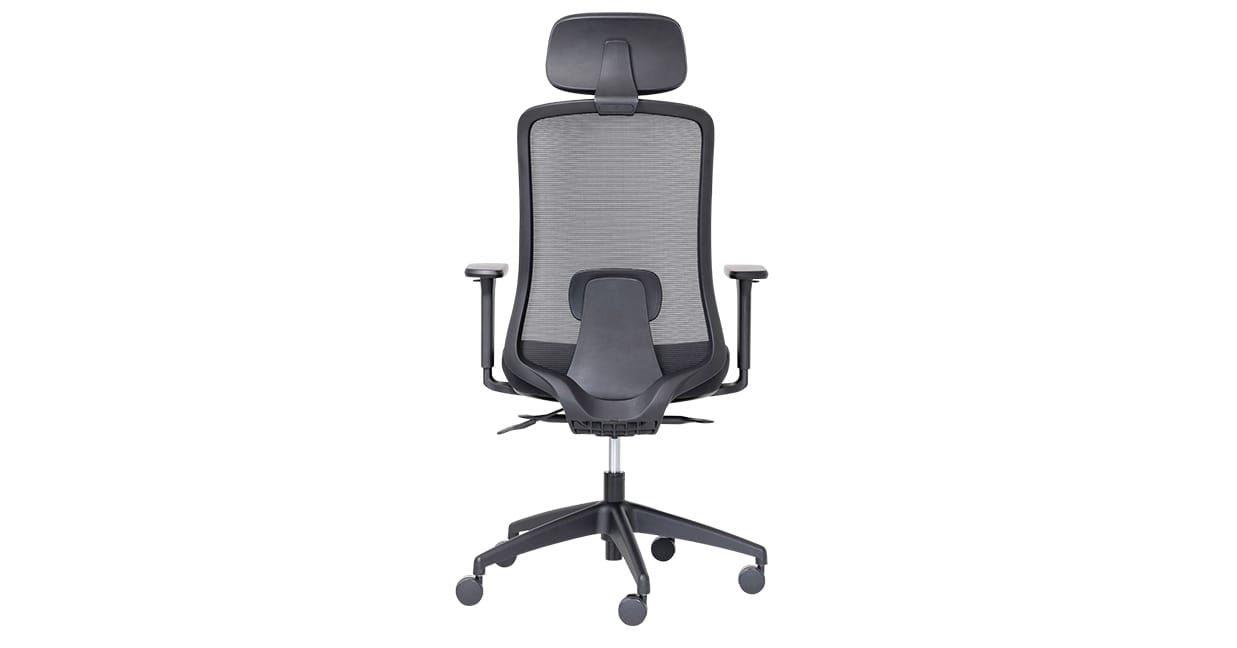

Example: Buro Elan with arms and headrest
8. Headrest
Some executive office chairs come equipped with a headrest to add extra protection against neck aches, pains and strains. Headrests benefit those who suffer from acute neck pain and unload weight during the day.
Many office chairs, like the Buro Elan and Buro Mentor, have optional add-ons including a headrest.
Ever wondered what all of those levers beneath your office chair actually do?
Your office chair may have several levers to help you adjust your seat angle, backrest and height. Levers give you full control of your ergonomic setup. Check out our Part Two Article, Ergonomic office chair adjustments explained - levers, mechanisms and more.




