Ever wondered what all of those levers beneath your office chair actually do?
Chair levers give you full control over your ergonomic setup, allowing you to adjust to a position that suits you.
Ergonomic office chairs come with several levers to adjust your seating with ease. Here’s a breakdown of what they do, and how they make you more comfortable.
Ergonomic chair lever adjustments
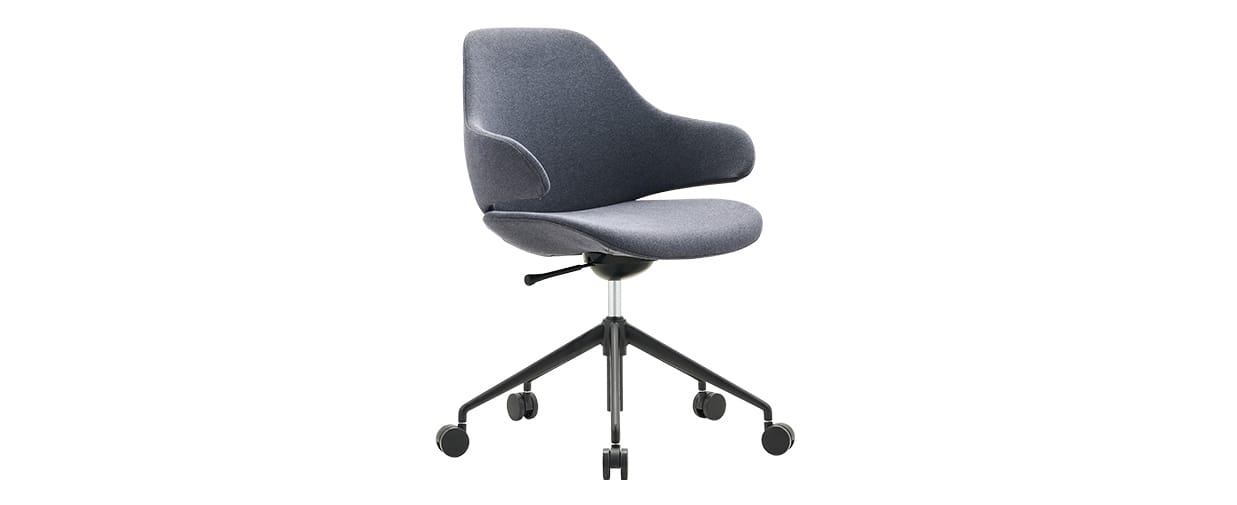

- Example: Konfurb Orbit Mid Back 5 Star Base
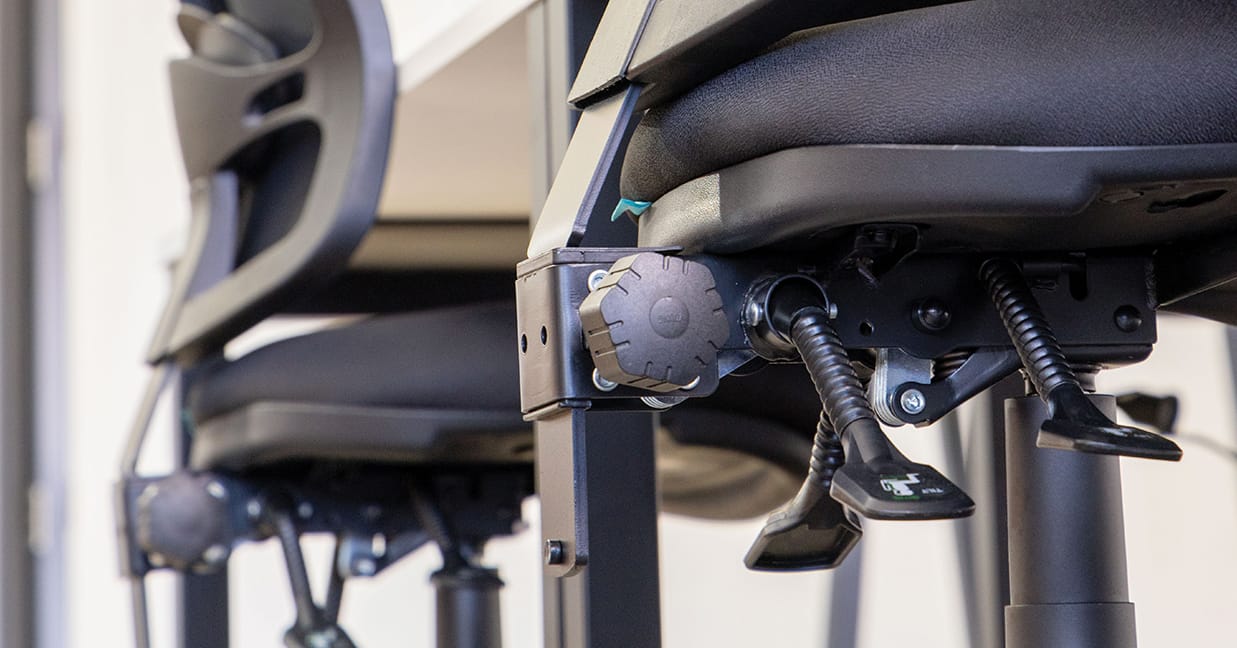
One lever mechanism
A one lever mechanism has a seat height adjustment and most chairs also come with a synchronised seat back tilt that can be locked with the same lever. Move it up and down to change the seat height and in and out to lock the back tilt. Examples: Konfurb Harmony (seat height only), Mondo Soho, Mondo Gene, Konfurb Orbit Mid Back 5 Star Base.
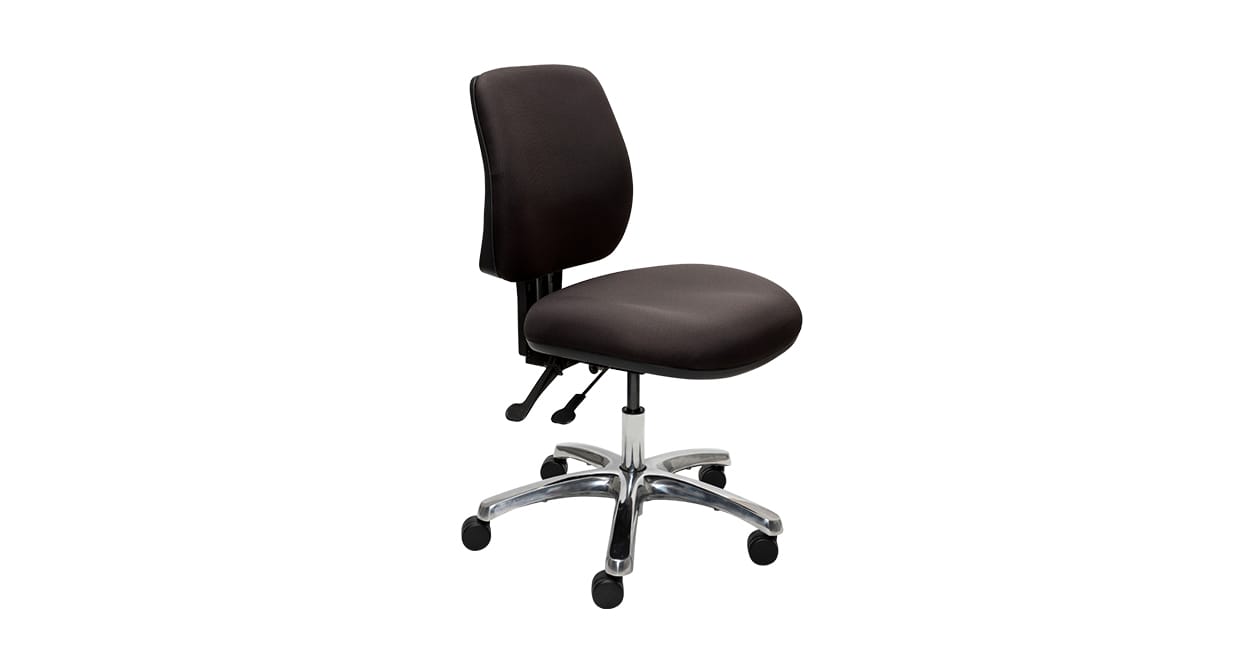

- Example: Buro Roma 2 Lever Mid Back
Two lever mechanisms
Two lever mechanisms come with a seat height adjustment, and a combined seat and back tilt adjustment, with a tilt lock to suit your needs.
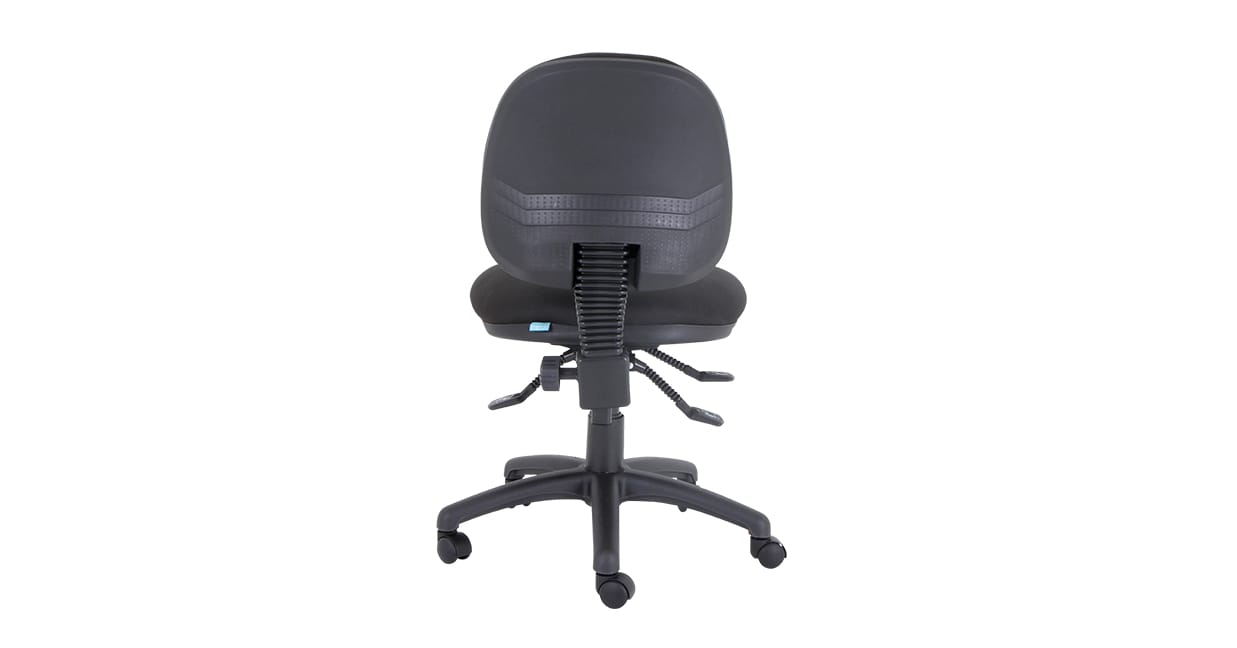

- Example: Mondo Java Mid Back
Three lever mechanisms
Three lever mechanisms have a seat height adjustment, independently adjustable seat tilt, and an independently adjustable back tilt. This extra lever allows you greater adjustability for a more open posture.
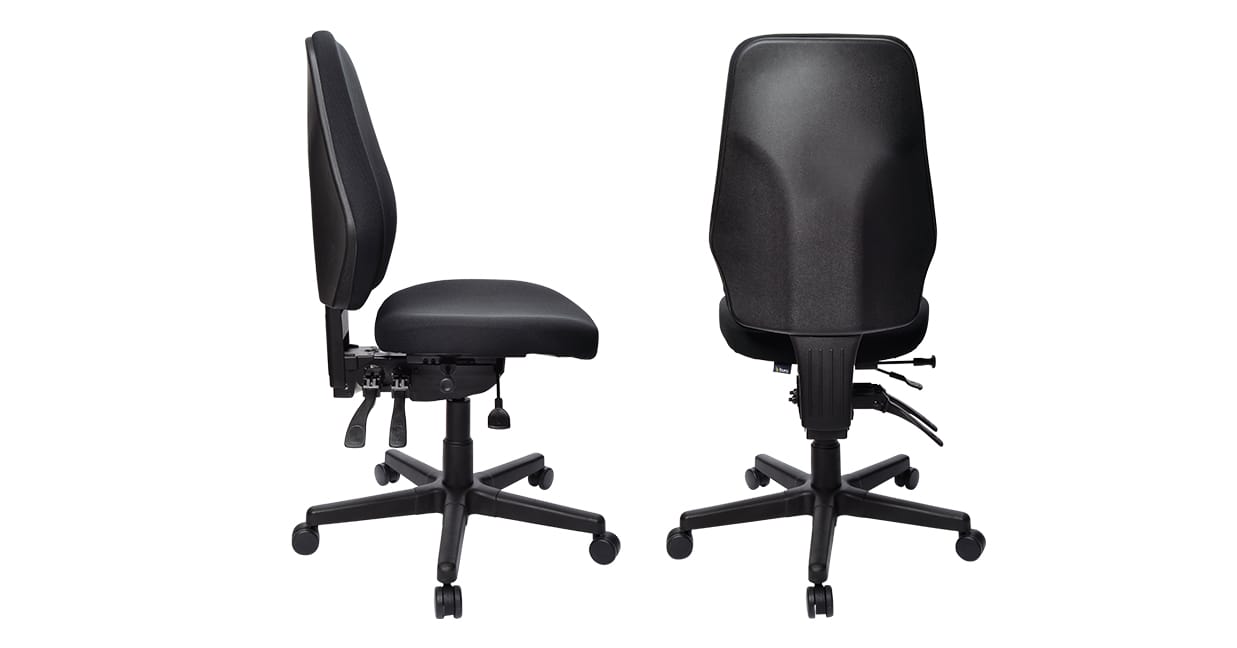

Example: Buro Aura Ergo +
Four lever mechanisms
The same as a three-lever mechanism, with seat height, independently adjustable seat tilt and back tilt, with the addition of a depth adjustable seat slide.

Example: Buro Elan
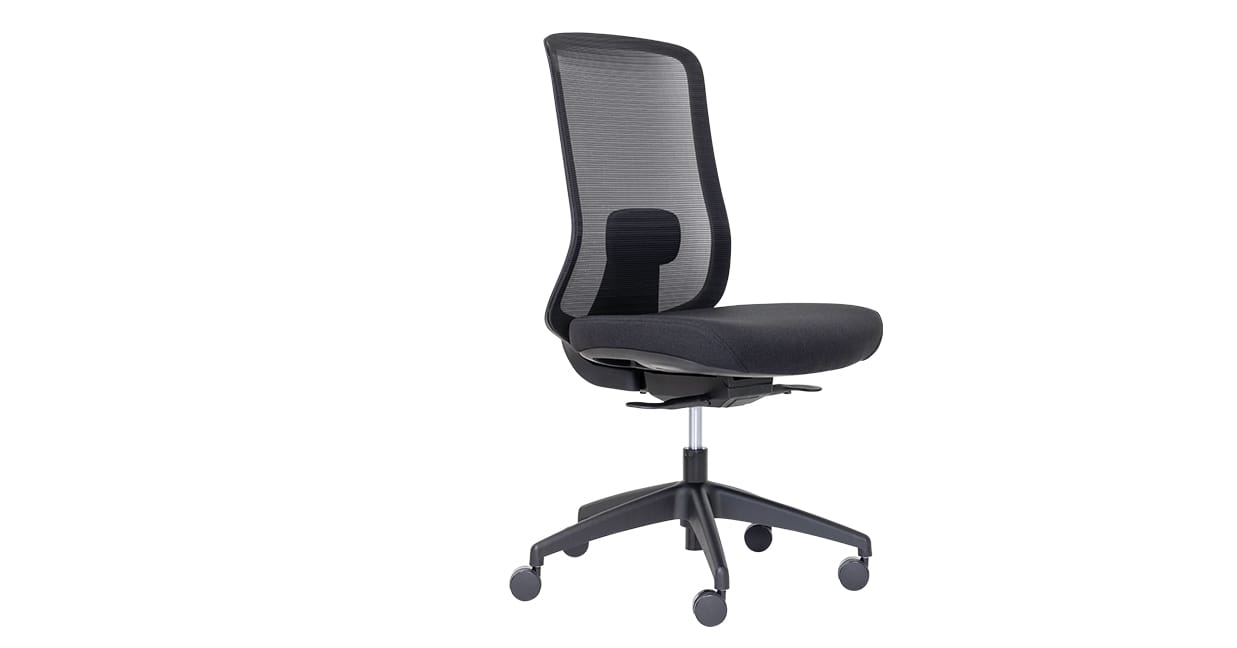
Synchro mechanism
Chairs with a synchro mechanism, like the Buro Elan, synchronise the backrest and seat tilt, so that they move together, keeping angles consistent for maximum support.
The beauty of these chairs is that when you move, the chair moves with you, encouraging good posture. There are no levers to adjust, apart from the seat height and seat slider, the mechanism does all the work!
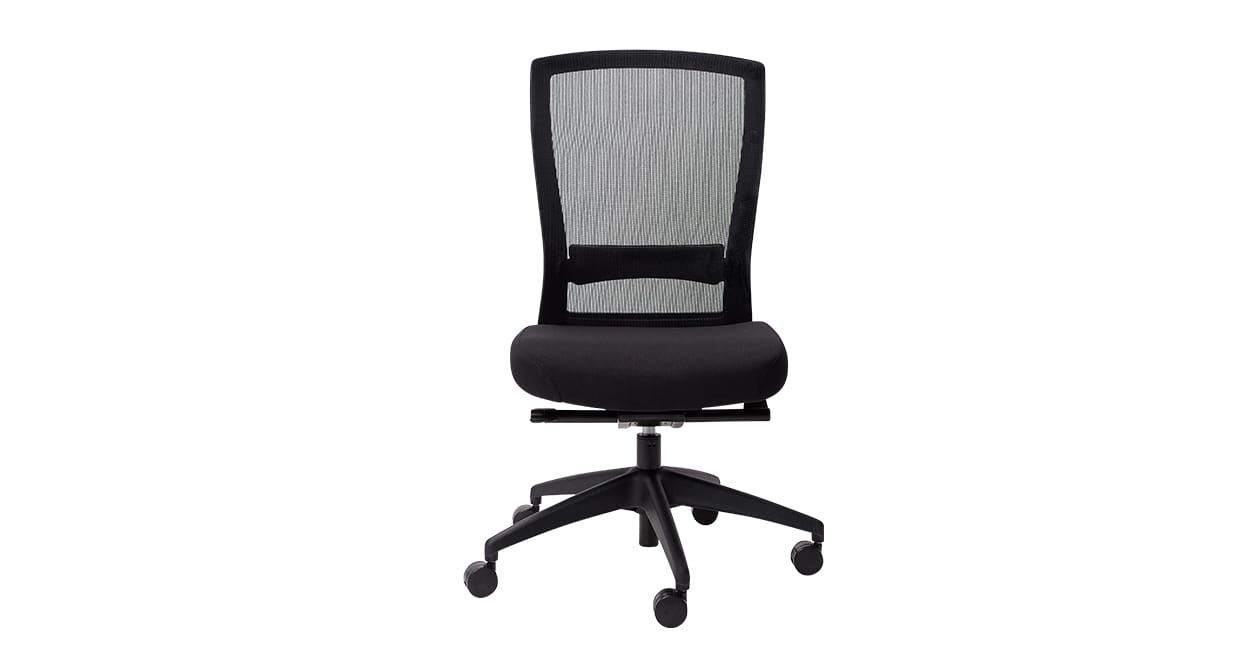
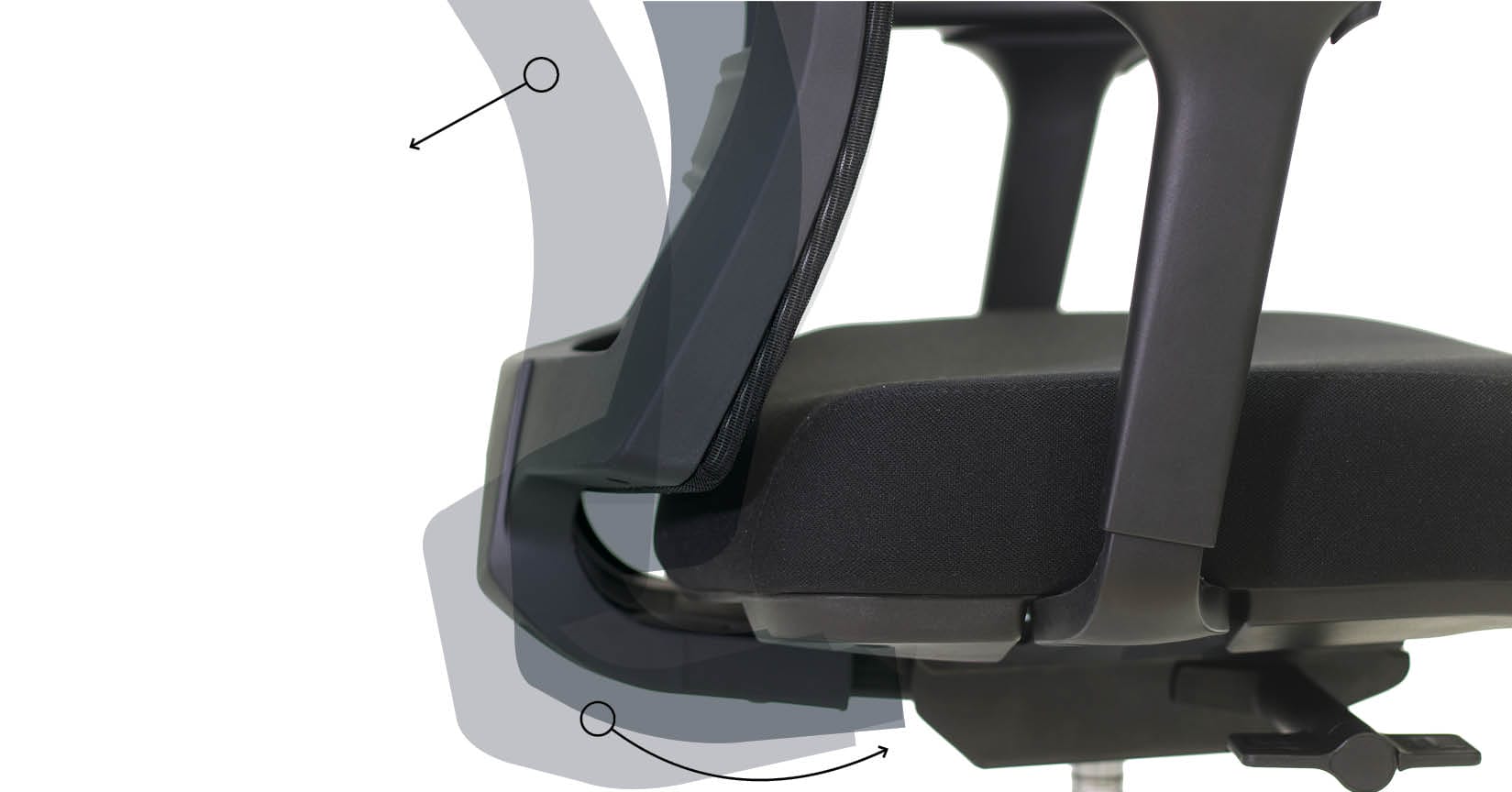


Example: Buro Mentor
Buro Dynamic Intelligence™ technology
Chairs featuring Buro’s state-of-the-art Dynamic Intelligence™ Technology, such as the Buro Mentor and Buro Vela (available through OfficeMax), intuitively respond to your weight and organic movement through a self-weight mechanism. It’s essentially a self-weighting synchro mechanism. These smart chairs encourage a neutral spine position.
Some synchro chairs are also self-weighting, but if your chair has Buro Dynamic Intelligence™ Technology, you know it will.
What each lever does
Office chairs have a range of adjustment levers to help you change your seat height, backrest tilt and height, or seat depth and seat tilt.
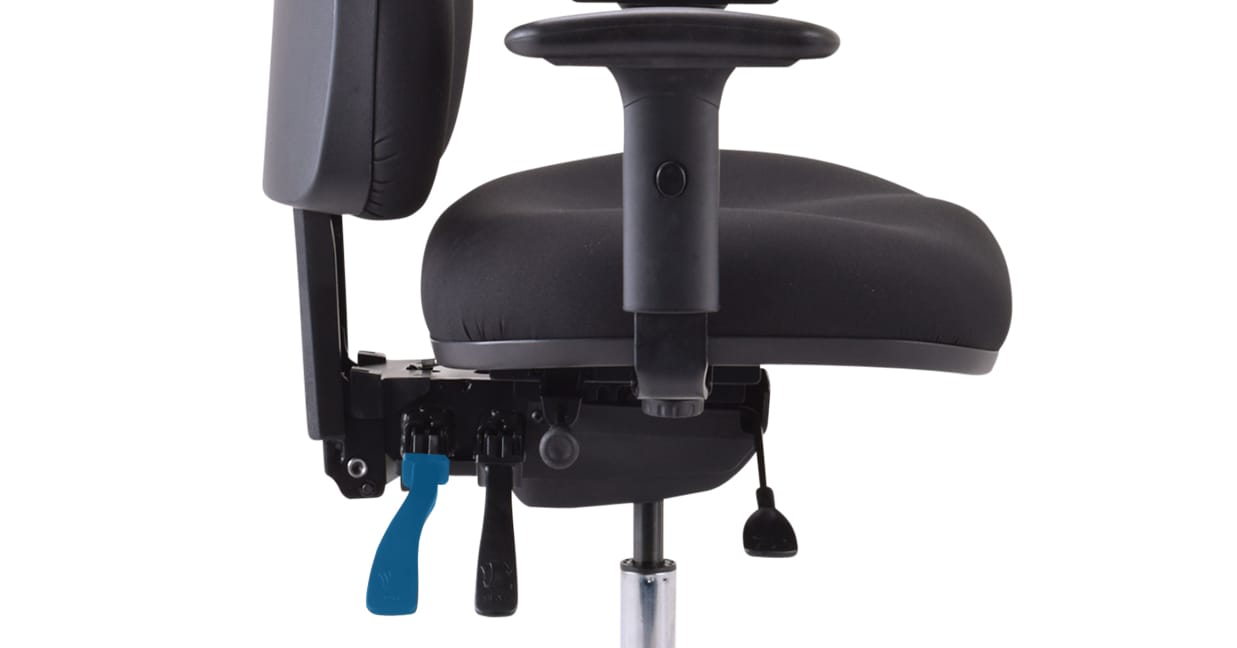

Backrest tilt lever on a Buro 3 lever chair
A five-star base has five points and five castors, and a four-point base has one fewer.
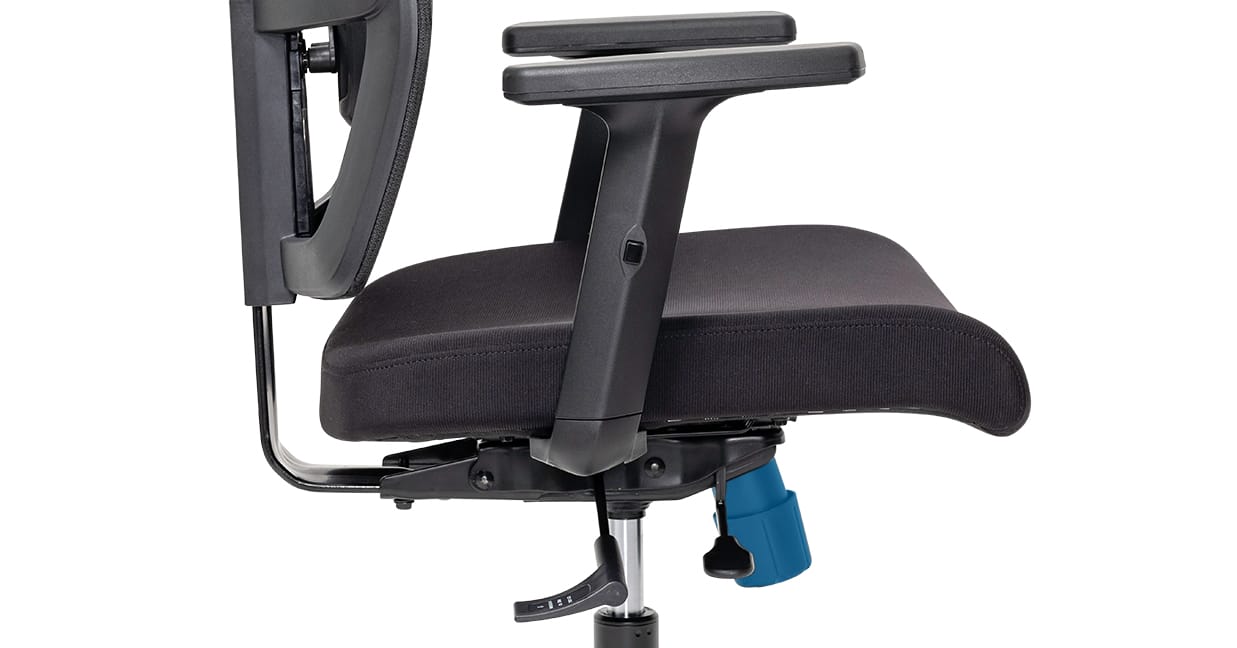

Example: Buro Mantra.
Body Weight Tension Adjustment: The tension setting, featured on chairs including the Buro Mantra, adjusts automatically to a person’s body weight.
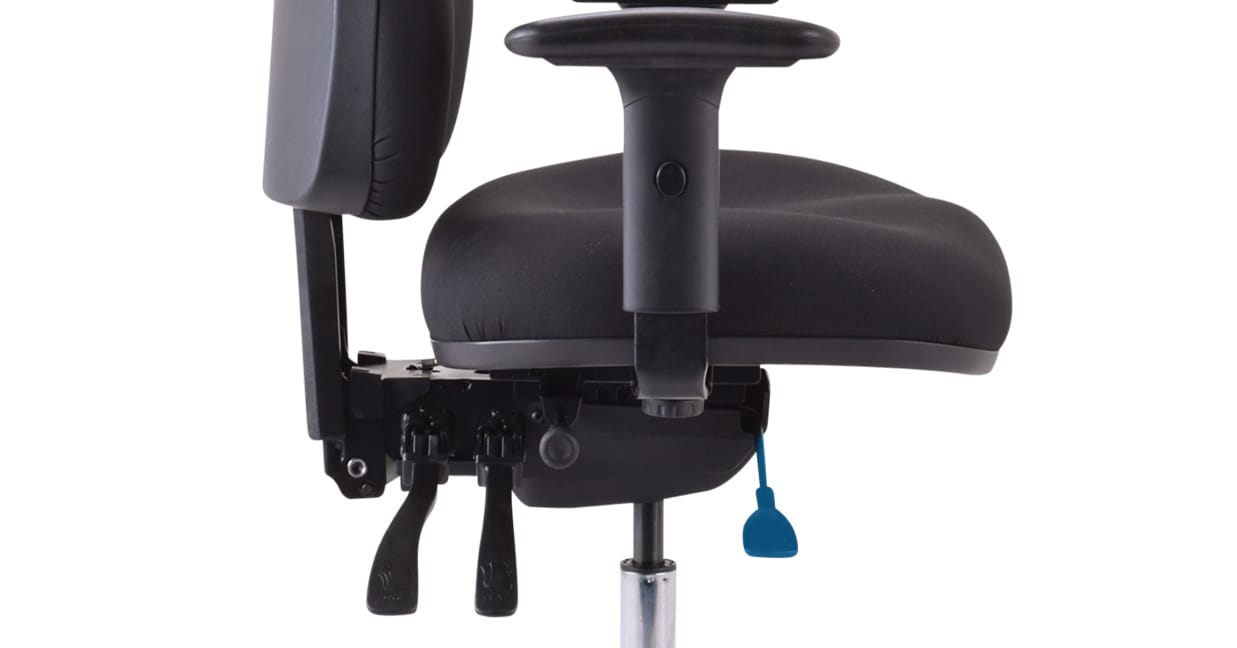

Seat height adjustment on a Buro 3 lever chair.
Seat Height: Adjusts the height of your chair. Watch video.
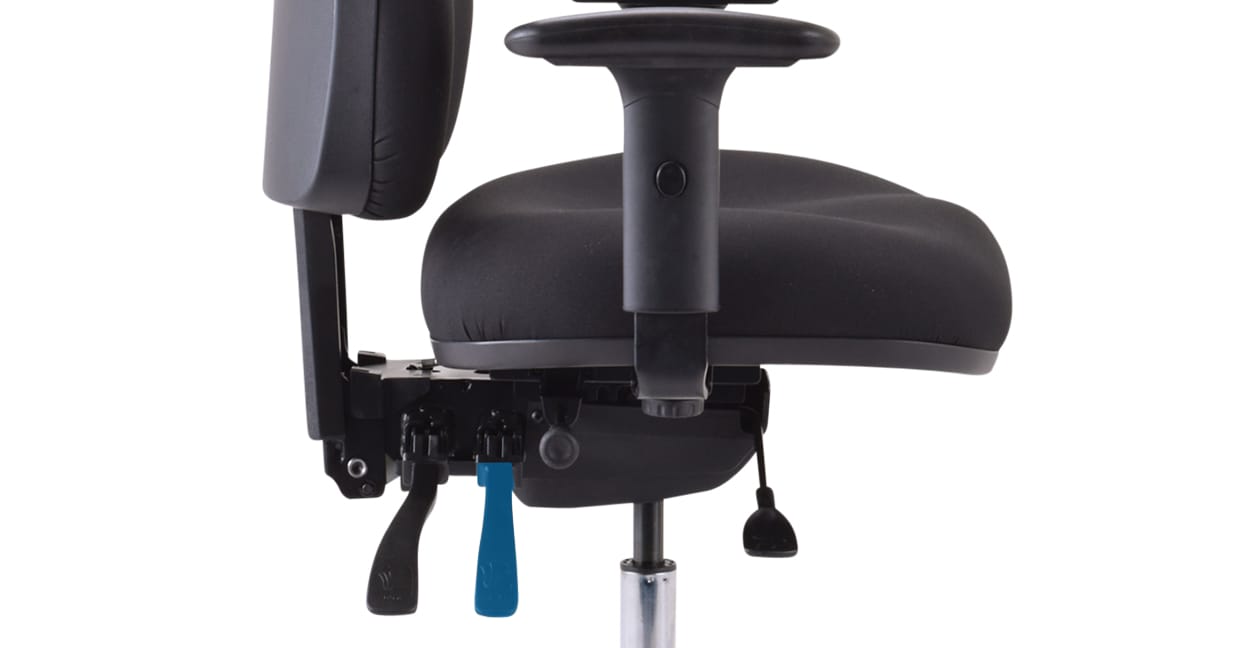

Seat tilt adjustment on a Buro 3 lever chair.
Seat Tilt: Changes the forward tilt of your seat and the angle of your legs.
On a 3 Lever chair it's the middle right lever. Watch video.
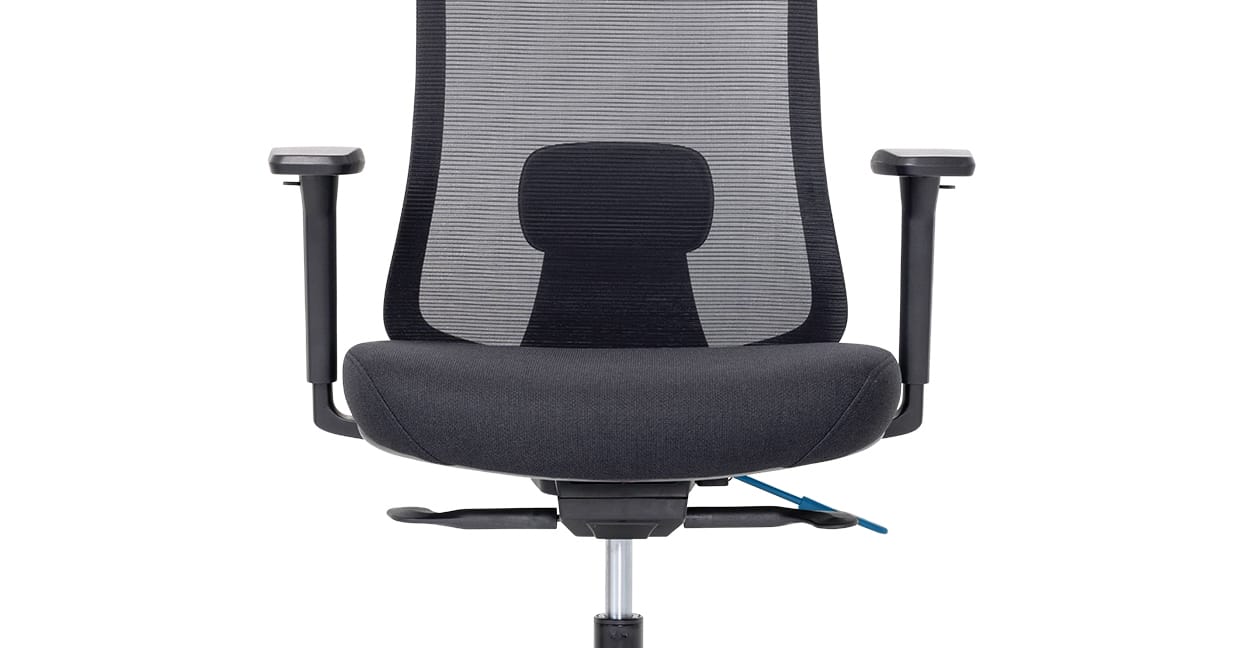

Example: Buro Elan
Seat Slider: Allows you to adjust the distance between your seat and the back of the office chair. Adjusting seat depth accommodates taller users and people with longer legs.
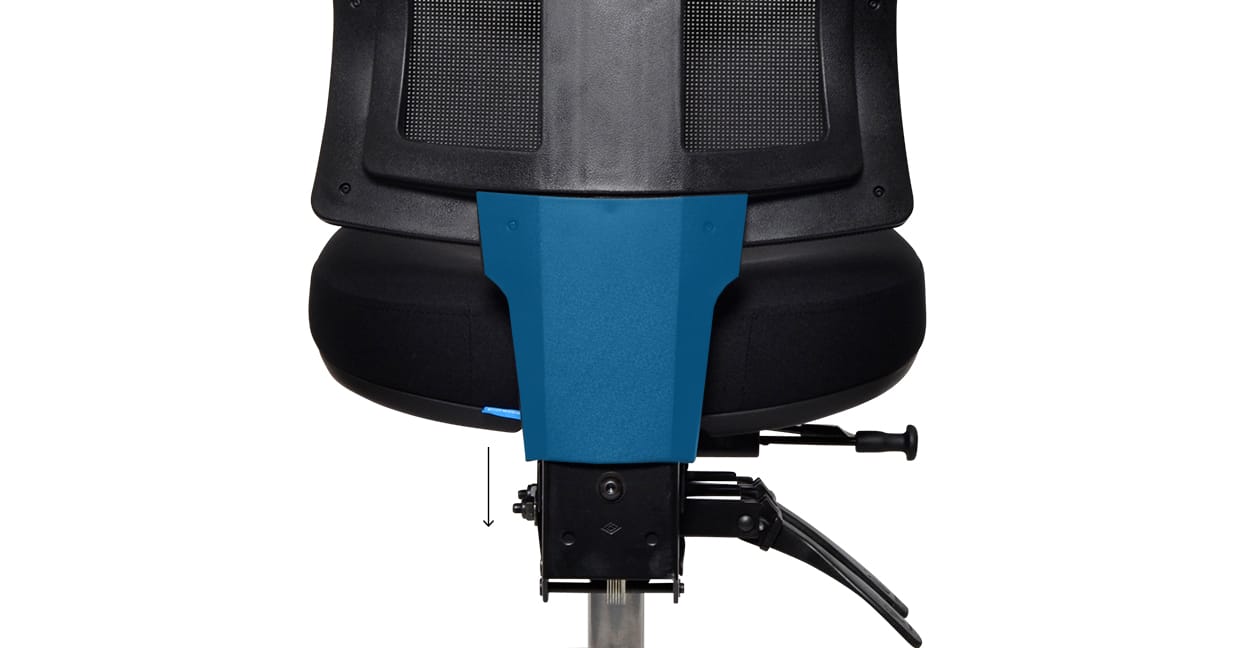

Back height adjustment on a Buro 3 lever chair
Back Height Adjustment: Moves your backrest up and down to match your height. Most Buro chairs come with a back height adjustment. Usually a ratchet back, which adjusts by simply lifting the entire backrest up and down. A few chairs use a manual knob adjustment. Watch video.
Ratchet: A simple mechanism allowing you to seamlessly lift your backrest up or down manually and click it into place.
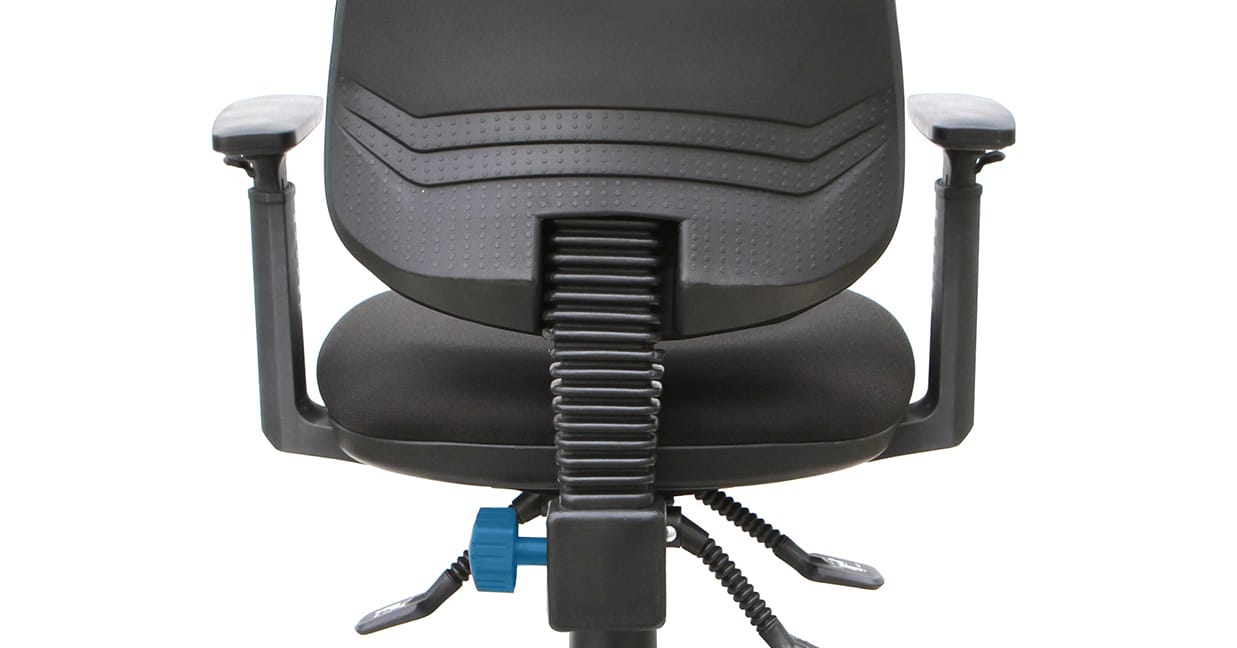

Example: Mondo Java High Back.
Manual back adjustments: Allow you to unfix your backrest manually, move it up or down, and re-lock it into place. Examples: Buro Image and Mondo Java.
Ever wondered what the castors, base and extra add-on accessories are all about?
Check out our article, Ergonomic office chair parts explained - castors, bases and more.